Custom Comparators and Coordinate Compression
自定义比较器与坐标压缩(Custom Comparators and Coordinate Compression)
核心内容:使用自定义比较器对自定义对象或值进行非默认顺序排序,以及将大范围值压缩到小范围
编程语言:C++
前置知识:青铜级(Bronze)- 排序入门(Introduction to Sorting)
白银级(Silver)- 有序数组的二分查找(Binary Search on a Sorted Array)
目录
1. 自定义排序(Custom Sorting)
参考资料(Resources)
参考资料来源 | 章节/主题 | 内容说明 |
|---|---|---|
IUSACO | 8 - 排序与比较器(Sorting & Comparators) | 本模块部分内容基于此资料 |
CPH(《Competitive Programming 3》) | 3.2 - 自定义结构体、比较函数(User-Defined Structs, Comparison Functions) | 简要概述 |
排序不仅适用于数字。例如,“虫洞排序(Wormhole Sort)”的许多解决方案都需要先按边的权重对边列表进行排序。
题目详情 - Wormhole Sort - Oldmoon OJ
以样例输入中的边为例:
1 2 9
1 3 7
2 3 10
2 4 3 排序后应得到:
2 4 3
1 3 7
1 2 9
2 3 10 以下将介绍几种实现该排序的方法。
内置数据结构(Built-In Data Structures)
对组(Pairs)
最直接的方法是使用pair<int, pair<int, int>>。在C++中比较这类对组时,会先比较第一个元素,仅当第一个元素相等时,才会将第二个元素作为“平局breaker”(即进一步比较第二个元素)。
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
constexpr int edge_num = 4;
vector<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> edges(edge_num);
// 存储边:first为权重,second的first和second分别为两个顶点
edges[0] = {9, {1, 2}};
edges[1] = {7, {1, 3}};
edges[2] = {10, {2, 3}};
edges[3] = {3, {2, 4}};
// 按默认规则排序(先比较权重,再比较顶点)
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
// 输出排序结果
for (auto &e : edges) {
cout << e.second.first << " " << e.second.second << " " << e.first << "\n";
}
return 0;
}数组(Arrays)
另一种选择是使用std::array或std::vector存储边的信息:
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
constexpr int edge_num = 4;
// 使用array存储每条边:{权重, 顶点1, 顶点2}
vector<array<int, 3>> edges(edge_num);
edges[0] = {9, 1, 2};
edges[1] = {7, 1, 3};
edges[2] = {10, 2, 3};
edges[3] = {3, 2, 4};
// 按默认规则排序(依次比较array的第0、1、2个元素)
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
// 输出排序结果
for (auto &e : edges) {
cout << e[1] << " " << e[2] << " " << e[0] << "\n";
}
return 0;
}比较器(Comparators)
大多数排序函数的核心逻辑是:若按升序排序,则将“值较小”的对象排在“值较大”的对象之前;若按降序排序,则反之。这一逻辑通过逐对比较两个对象实现。
在C++中,比较器必须遵循一系列规则。设比较器为compare,待比较的对象为x和y,则需满足:
1. 若x小于y,返回true;
2. 若x大于或等于y,返回false;
3. 若compare(x, y)为true,则compare(y, x)必须为false(反对称性);
4. 若compare(x, y)为true且compare(y, z)为true,则compare(x, z)必须为true(传递性)。
本质上,比较器的作用是判断在排序后的序列中,x是否应位于y的左侧。
警告(Warning):对于两个相等的对象,比较器必须返回
false,否则会导致未定义行为。
重载
这种方法实现最简单,但仅适用于对象(不适用于基本数据类型),且无法为同一类型的类定义多种比较方式。
以下使用该方法对上述4条边进行排序:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 定义Edge结构体表示边
struct Edge {
int a, b; // 两个顶点
int width; // 边的权重
};
// 重载operator<,按权重升序排序
bool operator<(const Edge &x, const Edge &y) {
return x.width < y.width;
}
int main() {
constexpr int edge_num = 4;
vector<Edge> edges(edge_num);
edges[0] = {1, 2, 9};
edges[1] = {1, 3, 7};
edges[2] = {2, 3, 10};
edges[3] = {2, 4, 3};
// 调用sort,自动使用重载的operator<
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
// 输出排序结果
for (auto &e : edges) {
cout << e.a << " " << e.b << " " << e.width << "\n";
}
return 0;
}也可以在类外部定义operator<:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 定义Edge结构体表示边
struct Edge {
int a, b; // 两个顶点
int width; // 边的权重
};
// 在结构体外部重载operator<
bool operator<(const Edge &x, const Edge &y) {
return x.width < y.width;
}
int main() {
constexpr int edge_num = 4;
vector<Edge> edges(edge_num);
edges[0] = {1, 2, 9};
edges[1] = {1, 3, 7};
edges[2] = {2, 3, 10};
edges[3] = {2, 4, 3};
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
for (auto &e : edges) {
cout << e.a << " " << e.b << " " << e.width << "\n";
}
return 0;
}比较函数(Comparison Function)
我们也可以将比较器作为lambda表达式直接传入std::sort。这种方法的优势是:既适用于基本数据类型,也适用于类。
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 定义Edge结构体表示边
struct Edge {
int a, b; // 两个顶点
int width; // 边的权重
};
int main() {
constexpr int edge_num = 4;
vector<Edge> edges(edge_num);
edges[0] = {1, 2, 9};
edges[1] = {1, 3, 7};
edges[2] = {2, 3, 10};
edges[3] = {2, 4, 3};
// 传入lambda表达式作为比较器,按权重升序排序
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end(), [](const Edge &x, const Edge &y) {
return x.width < y.width;
});
// 输出排序结果
for (auto &e : edges) {
cout << e.a << " " << e.b << " " << e.width << "\n";
}
return 0;
}排序变体(Variations)
降序排序(Sorting in Descending Order)
实现降序排序有多种方法:
1. 先排序再反转:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5};
// 先按升序排序
sort(begin(nums), end(nums));
// 反转序列,得到降序
reverse(begin(nums), end(nums));
return 0;
}2. 使用反向迭代器:
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5};
// 直接通过反向迭代器按降序排序
sort(rbegin(nums), rend(nums));
return 0;
}3. 使用greater<>(适用于已定义operator>的数据结构,如对组、数组):
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <functional> // 包含greater<>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<pair<int, int>> pairs = {{1, 2}, {3, 1}, {2, 4}};
// 使用greater<>按降序排序
sort(pairs.begin(), pairs.end(), greater<>());
return 0;
4. 修改自定义operator<:若自行重载operator<,可将所有x.w < y.w替换为x.w > y.w,实现降序:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int a, b;
int width;
};
// 重载operator<,按权重降序排序
bool operator<(const Edge &x, const Edge &y) {
return x.width > y.width;
}
int main() {
vector<Edge> edges = {{1,2,9}, {1,3,7}, {2,3,10}, {2,4,3}};
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
for (auto &e : edges) {
cout << e.a << " " << e.b << " " << e.width << "\n";
}
return 0;
}多条件排序(Sorting by Multiple Criteria)
假设我们需要对Edge列表进行排序:主条件为权重升序,次条件为第一个顶点a升序。实现逻辑与单条件排序类似:若权重不相等,则按权重比较;若权重相等,则按第一个顶点比较。
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int a, b; // 顶点1、顶点2
int width; // 权重
};
int main() {
// 修改后的样例输入(包含权重相等的边)
vector<Edge> edges = {
{2, 2, 7},
{1, 3, 7},
{2, 3, 10},
{2, 4, 3}
};
// 多条件比较器:先比权重,再比顶点a
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end(), [](const Edge &x, const Edge &y) {
if (x.width != y.width) {
// 主条件:权重升序
return x.width < y.width;
} else {
// 次条件:顶点a升序
return x.a < y.a;
}
});
// 输出排序结果:权重3和10的边位置不变,权重7的两条边按顶点a交换顺序
for (auto &e : edges) {
cout << e.a << " " << e.b << " " << e.width << "\n";
}
return 0;
}2. 坐标压缩(Coordinate Compression)
坐标压缩指将列表中的每个值映射为“该值在列表排序后的索引”的过程。例如,列表{7, 3, 4, 1}排序后为{1, 3, 4, 7},其压缩结果为{3, 1, 2, 0}——其中1是原列表中最小的值,对应索引0;7是原列表中最大的值,对应索引3(排序后列表的最大索引)。
当处理的数值范围极大,但我们仅关心它们的相对顺序(例如,只需判断一个值是否大于另一个值)时,坐标压缩是简化实现的有效方法。例如,若有一组取值范围为0到10^9的整数,直接将其作为数组索引会导致数组大小需达到10^9,进而触发“内存超限(MLE)”错误;但如果这组整数的数量仅为N ≤ 10^6,通过坐标压缩可将其映射到0到N-1的范围,此时即可安全地作为数组索引使用。
示例1(Example 1)
坐标压缩的典型应用场景是USACO的“矩形牧场(Rectangular Pasture)”问题。此处不深入完整解题逻辑,仅聚焦坐标压缩的应用:由于该问题需使用“二维前缀和”(白银级知识点),将所有点的坐标压缩到0到N-1的范围,可使其直接作为数组索引。若不进行坐标压缩,创建足够大的数组会导致“内存超限(Memory Limit Exceeded)”。
以下是“矩形牧场”问题的解决方案(开头部分包含坐标压缩逻辑),注意如何使用自定义比较器对顶点进行排序:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> Point; // 点的坐标(x, y)
// 自定义比较器:按y坐标升序排序
bool ycomp(Point p, Point q) { return p.second < q.second; }
const int MAX_N = 2500;
int pref[MAX_N + 1][MAX_N + 1]; // 二维前缀和数组
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<Point> pts(N);
vector<int> xs(N); // 存储所有x坐标,用于压缩
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> pts[i].first >> pts[i].second;
xs[i] = pts[i].first;
}
// 坐标压缩:x坐标
sort(xs.begin(), xs.end());
// 去重(保留唯一值)
xs.erase(unique(xs.begin(), xs.end()), xs.end());
// 将每个点的x坐标替换为压缩后的索引
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// 二分查找x坐标在xs中的位置(即压缩后的索引)
pts[i].first = lower_bound(xs.begin(), xs.end(), pts[i].first) - xs.begin();
}
// 按y坐标排序(后续前缀和计算需要)
sort(pts.begin(), pts.end(), ycomp);
// 后续二维前缀和计算逻辑...
return 0;
}在“矩形牧场”问题的解决方案中,坐标被直接替换为压缩后的值,原始坐标因不再需要而被忽略。但在某些问题中,我们可能需要同时保留原始坐标和压缩后的值。
示例2(Example 2)
问题背景:静态区间查询(Static Range Queries)
难度:CF - 困难(Hard)
涉及知识点:前缀和、坐标压缩
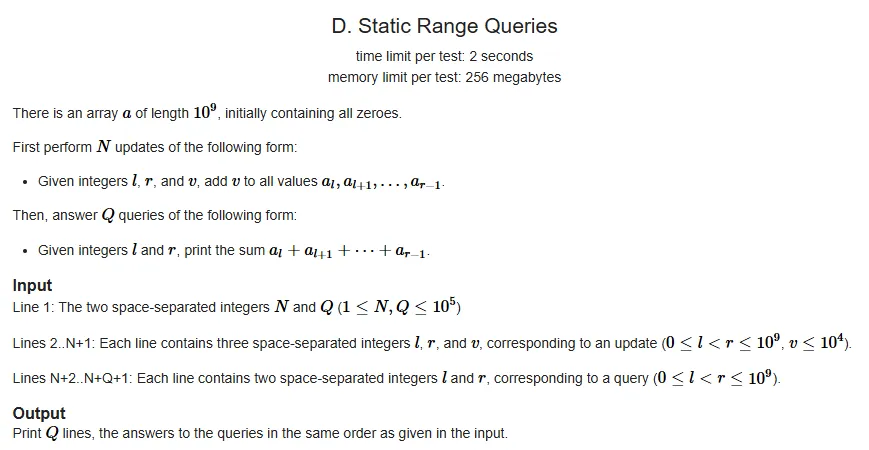
该问题的坐标压缩实现需“保留原始值”(而非像上一个问题那样直接替换)。若仅关注坐标压缩的实现逻辑(以及压缩索引与原始值的转换),可参考以下简化代码:
indices:存储需要压缩的所有值;对
indices排序并去重后,即可用于压缩;getCompressedIndex函数:输入原始值,通过二分查找其在indices中的位置,得到压缩后的索引;从“压缩索引”转换为“原始值”:直接访问
indices中对应索引的元素即可。
以下是更详细的代码解释:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll difference_array[400005];
// 差分数组:difference_array[i]表示区间i-1和i之间的数值差
// 获取压缩后的索引
int getCompressedIndex(const vector<ll> &indices, ll val) {
// 二分查找val在indices中的位置
return lower_bound(indices.begin(), indices.end(), val) - indices.begin();
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int Q;
cin >> Q;
vector<ll> queries[2]; // 存储查询的左右边界
vector<ll> all_vals; // 存储所有需要压缩的值
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) {
ll L, R;
cin >> L >> R;
queries[0].push_back(L);
queries[1].push_back(R);
all_vals.push_back(L);
all_vals.push_back(R + 1); // 区间处理需要,避免边界问题
}
// 坐标压缩步骤1:排序
sort(all_vals.begin(), all_vals.end());
// 坐标压缩步骤2:去重
all_vals.erase(unique(all_vals.begin(), all_vals.end()), all_vals.end());
// 处理查询(示例:使用差分数组统计区间覆盖)
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) {
ll L = queries[0][i];
ll R = queries[1][i];
// 将原始边界转换为压缩后的索引
int l = getCompressedIndex(all_vals, L);
int r = getCompressedIndex(all_vals, R + 1);
// 差分数组更新
difference_array[l]++;
difference_array[r]--;
}
// 后续差分数组前缀和计算、结果处理...
return 0;
}3. 练习题(Problems)
实用技巧(Pro Tip):以下许多题目可能会用到其他白银级知识点,例如前缀和。
状态(Status) | 来源(Source) | 题目名称(Problem Name) | 难度(Difficulty) | 标签(Tags) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
- | CSES | 餐厅顾客(Restaurant Customers) | 简单(Easy) | 显示标签(Show Tags):前缀和(Prefix Sums)、排序(Sorting) |
- | CF(Codeforces) | 覆盖点计数(Covered Points Count) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):坐标压缩(Coordinate Compression)、前缀和(Prefix Sums)、排序(Sorting) |
- | 白银级(Silver) | 救生员(Lifeguards) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):前缀和(Prefix Sums)、排序(Sorting) |
- | 白银级(Silver) | 租赁服务(Rental Service) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):前缀和(Prefix Sums)、排序(Sorting) |
- | 白银级(Silver) | 山景(Mountain View) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):排序(Sorting) |
- | 白银级(Silver) | 陷入车辙(Stuck in a Rut) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):排序(Sorting) |
- | 黄金级(Gold) | 分割田地(Splitting the Field) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):前缀和(Prefix Sums)、排序(Sorting) |
- | CF(Codeforces) | 最小字符串拼接(The Smallest String Concatenation) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):排序(Sorting) |
- | CF(Codeforces) | 内扎尔与对称数组(Nezzar and Symmetric Array) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):前缀和(Prefix Sums)、排序(Sorting) |
- | CF(Codeforces) | 正确放置(Correct Placement) | 中等(Normal) | 显示标签(Show Tags):排序(Sorting) |
- | 白银级(Silver) | 三角形(Triangles) | 困难(Hard) | 显示标签(Show Tags):排序(Sorting) |
- | 白银级(Silver) | 排序混乱(Out Of Sorts) | 困难(Hard) | 显示标签(Show Tags):排序(Sorting) |
- | 白银级(Silver) | 会面(Meetings) | 极难(Very Hard) | 显示标签(Show Tags):排序(Sorting) |