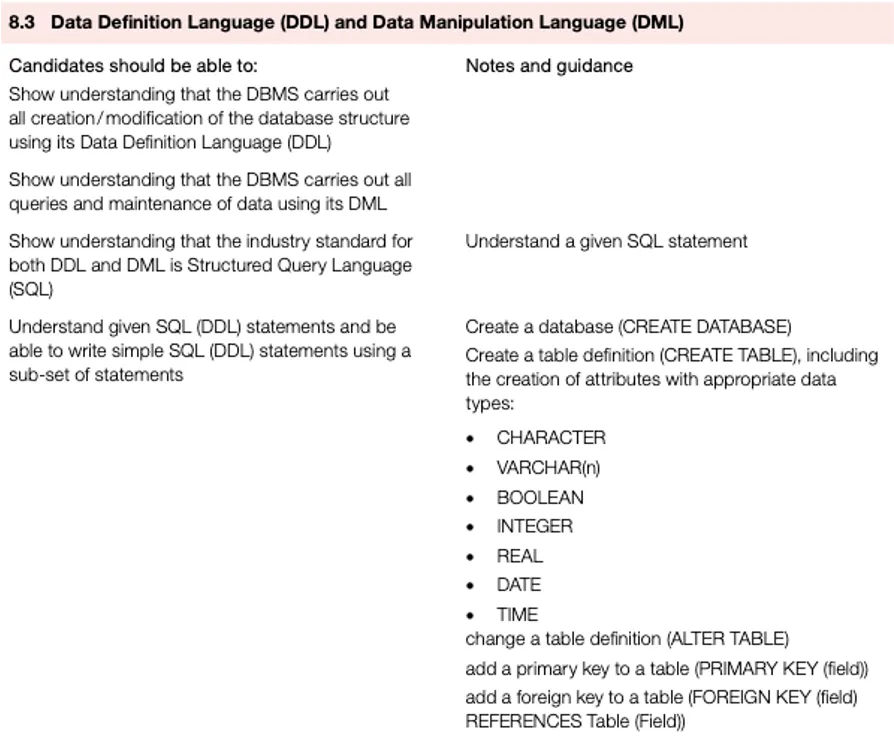
DDL DML
Online SQL
https://sql.js.org/examples/GUI/
Industry standard methods for building and modifying a database
DBMSs use a data definition language (DDL) to create, modify and remove the data structures that form a relational database. DDL statements are written as a script that uses syntax similar to a computer program.
DML statements are written in a script that is similar to a computer program.
These languages have different functions: DDL is used for working on the relational database structure, whereas DML is used to work with the data stored in the relational database.
DBMSs use a data manipulation language (DML) to add, modify, delete and retrieve the data stored in a relational database.
Most DBMSs use structured query language (SQL) for both data definition and data manipulation. SQL was developed in the 1970s and since then it has been adopted as an industry standard.
DBMSs use a (DDL) to create, modify and remove the data structures that form a relational database. DDL statements are written as a script that uses syntax similar to a computer program
SQL (DDL) commands and scripts
In order to be able to understand and write SQL, you should have practical experience of writing SQL scripts.
There are many applications that allow you to do this.
For example, MySQL and SQLite are freely available ones.
When using any SQL application it is important that you check the commands available to use as these may differ slightly from those listed below.
SQL operators
Operator | Description |
|---|---|
= | equal to |
> | greater than |
< | less than |
>= | greater than or equal to |
<= | less than equal to |
<> | not equal to |
BETWEEN | between a range of two values |
LIKE | search for a pattern |
IN | specify multiple values |
AND | specify multiple conditions that must all be true |
OR | specify multiple conditions where one or more conditions must be true |
NOT | specify a condition that must be false |
CREATE DATABASE
-- CREATE DATABASE databasename;
CREATE DATABASE School;CREATE TABLE
-- CREATE TABLE table_name (
-- column1 datatype,
-- column2 datatype,
-- column3 datatype,
-- ....
-- );
CREATE TABLE Student (
ID integer NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
Age integer
);ALTER TABLE
-- ALTER TABLE table_name
-- ADD column_name datatype;
-- DROP COLUMN column_name;
ALTER TABLE Student
ADD FirstName varchar(255);
DROP COLUMN Age;PRIMARY KEY
CREATE TABLE Student (
ID integer NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age integer,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);FOREIGN KEY ...REFERENCES
CREATE TABLE Student (
ID integer NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age integer,
ClassID integer,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
FOREIGN KEY (ClassID) REFERENCES Class(ID)
);Data types for attributes | Description |
|---|---|
SQL (DDL) command | Description |
CREATE DATABASE | Creates a database |
CREATE TABLE | Creates a table definition |
ALTER TABLE | Changes the definition of a table |
PRIMARY KEY | Adds a primary key to a table |
FOREIGN KEY ...REFERENCES | Adds a foreign key to a table |
CHARACTER | Fixed length text |
VARCHAR() | Variable length text |
BOOLEAN | True or False; SQL uses the integers 1 and 0 |
INTEGER | Whole number |
REAL | Number with decimal places |
DATE | A date usually formatted as YYYY-MM-DD |
TIME | A time usually formatted as HH:MM:SS |
SELECT FROM
SELECT LastName, Age FROM Student;WHERE
SELECT LastName, Age FROM Student
WHERE Age > 10;ORDER BY
SELECT LastName, Age FROM Student
WHERE Age > 10
ORDER BY Age;GROUP BY
SELECT AVG(Age), ClassID
FROM Student
GROUP BY ClassID;INNER JOIN
SELECT FirstName, ClassID
FROM Student
WHERE FirstName <> ""
INNER JOIN Class ON Student.ClassID = Class.ID;AND
SELECT FirstName, ClassID
FROM Student,Class
WHERE FirstName <> ""
AND Student.ClassID = Class.ID;SUM
SELECT SUM(Age)
FROM StudentCOUNT
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM StudentAVG
SELECT AVG(Age)
FROM StudentSQL(DML) query command | Description |
|---|---|
SQL(DML) query command | Description |
SELECT FROM | Fetches data from a database. Queries always beginwith SELECT. |
WHERE | Includes only rows in a query that match a given condition |
ORDER BY | Sorts the results from a query by a given column eitheralphabetically or numerically |
GROUP BY | Arranges data into groups |
INNER JOIN | Combines rows from different tables if the joincondition is true |
SUM | Returns the sum of all the values in the column |
COUNT | Counts the number of rows where the column is not NUL |
AVG | Returns the average value for a column with a numericdata type |
INSERT INTO | Adds new row(s) to a table |
DELETE FROM | Removes row(s) from a table |
UPDATE | Edits row(s) in a table |
INSERT INTO
-- INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
-- VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
INSERT INTO Student (FirstName, LastName, Age, ClassID)
VALUES ("Frank", "Oldmoon", 18, 1);DELETE FROM
-- DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
DELETE FROM Student WHERE Age > 18;UPDATE
-- UPDATE table_name
-- SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
-- WHERE condition;
UPDATE Student
SET Age = 12
WHERE LastName = "Oldmoon";