AI
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a machine or application which carries out a task that requires some degree of intelligence when carried out by a human being. These tasks could include:
the use of a language
carrying out a mathematical calculation or function
recognising a person’s face
the ability to operate machinery, such as a car, an aeroplane or a train
analysing data to predict the outcome of a future event, such as weather forecasting
The impact of AI
People often associate AI with science fiction, fantasy and robots.
Numerous films and books fuel this association.
The science fiction author, Isaac Asimov, went so far as to produce his own three laws of robotics:
1. A robot may not injure a human through action or inaction.
2. A robot must obey orders given by humans without question.
3. A robot must protect itself unless it conflicts with the two laws above.
However, AI goes way beyond robotics.
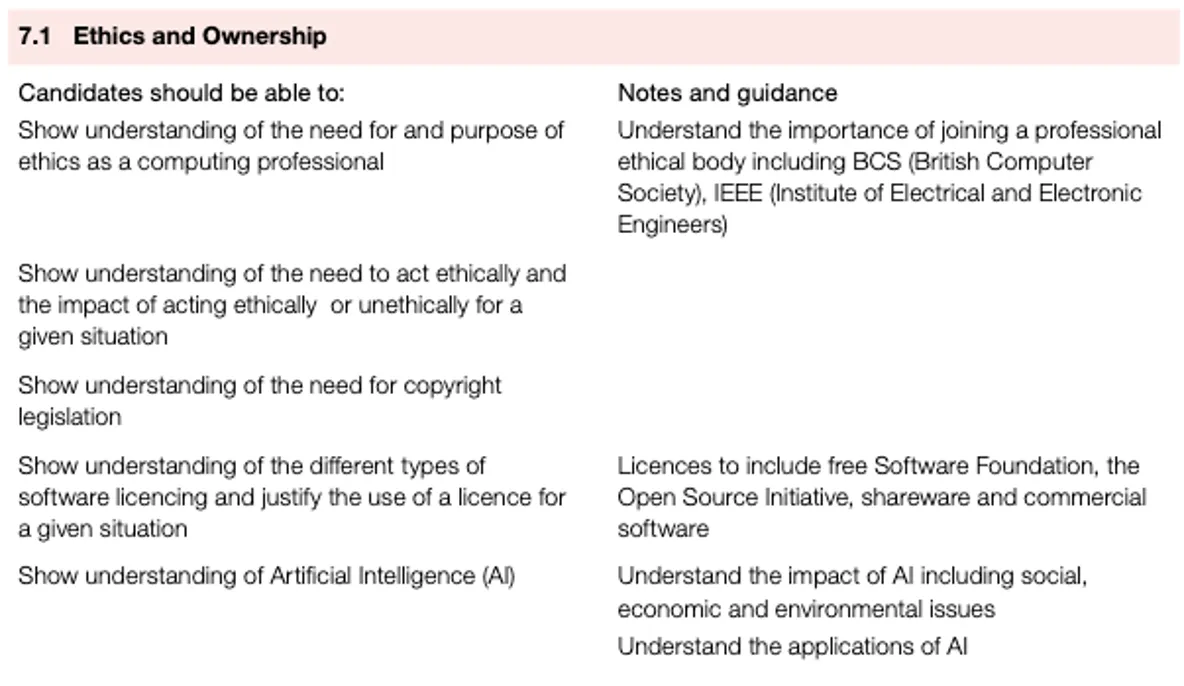
autonomous (driverless) vehicles
artificial limb technology
drones, used to carry out dangerous or unpleasant tasks such as bomb disposal, welding, or entering nuclear disaster areas
climate change predictions
medical procedures, such as eye operations where extreme precision is required.
It covers a number of areas, such as:
The impacts of AI on society, the economy and the environment
Transport
Some taxi companies are already looking at the introduction of autonomous (driverless) cars.
A customer can call up the taxi using an app on their mobile phone, which also automatically handles the payment.
Criminal justice system
Advances in facial recognition systems is making fingerprinting in forensic science almost obsolete.
AI is also being used to automate legal work and some courts in the USA have trialled the use of AI to sentence criminals and even decide if a prisoner is eligible for parole.
(AI) is a machine or application which carries out a task that requires some degree of intelligence when carried out by a human being.
Choose three different examples of AI