Program Designs

Structure chart
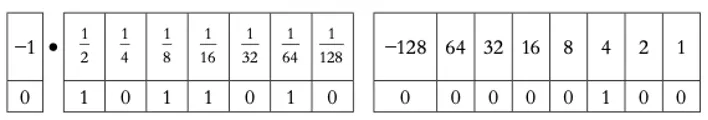
A structure chart is a modelling tool used in program design to decompose a problem into a set of sub-tasks.
The structure chart shows the hierarchy or structure of the different modules and how they connect and interact with each other.
Each module is represented by a box and the parameters passed to and from the modules are shown by arrows pointing towards the module receiving the parameter.
Each level of the structure chart is a refinement of the level above.
A structure chart for converting a temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius.
The top level shows the name for the whole task that is refined into three sub-tasks or modules shown on the next level.
Selection
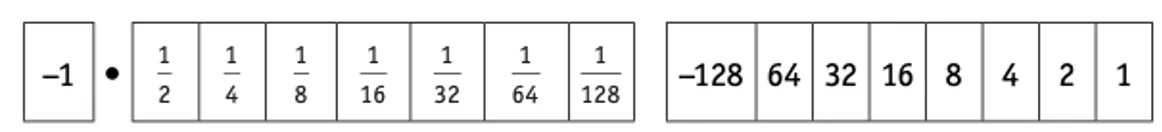
Structure charts can also show selection.
The temperature conversion task above could be extended to either convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius or Celsius to Fahrenheit using the diamond shaped box to show a condition that could be true or false.
Repetition
Structure charts can also show repetition.
The temperature conversion task above could be extended to repeat the conversion until the number 999 is input.
The repetition is shown by adding a labelled semi-circular arrow above the modules to be completed.
Once a structure chart has been completed, it can be used to derive a pseudocode algorithm.
A is a modelling tool used in program design to decompose a problem into a set of sub-tasks
Finite state machine (FSM)
A finite state machine (FSM) is a mathematical model of a machine that can be in one of a fixed set of possible states.
One state is changed to another by an external input, this is called a transition.
A diagram showing the behaviour of an FSM is called a state-transition diagram.

State-transition diagrams
State-transition diagrams show the conditions needed for an event or events that will cause a transition to occur, and the outputs or actions carried out as the result of that transition.
State-transition diagrams can be constructed as follows:
States are represented as nodes (circles).
Transitions are represented as interconnecting arrows.
Events are represented as labels on the arrows.
Conditions can be specified in square brackets after the event label.
The initial state is indicated by an arrow with a black dot.
A stopped state is indicated by a double circle.
The algorithm for unlocking a door using a three-digit entry code can be represented by a state-transition diagram.
If the door is unlocked with a three- digit entry code, the lock can be in four states
locked and waiting for the input of the first digit
waiting for the input of the second digit
waiting for the input of the third digit
unlocked.
If an incorrect digit is input, then the door returns to the locked state.
The algorithm halts when the door is unlocked.
A state-transition table shows every state, each possible input and the state after the input.
The state-transition table for a door with the entry code 259 is shown below.
Current state | Event | Next state |
|---|---|---|
locked | 2 input | waiting for input of 2nd digit |
locked | not 2 input | locked |
waiting for input of 2nd digit | 5 input | waiting for input of 3rd digit |
waiting for input of 2nd digit | not 5 input | locked |
waiting for input of 3rd digit | 9 input | unlocked and stopped |
waiting for input of 3rd digit | not 9 input | locked |

A is a mathematical model of a machine that can be in one of a fixed set of possible states