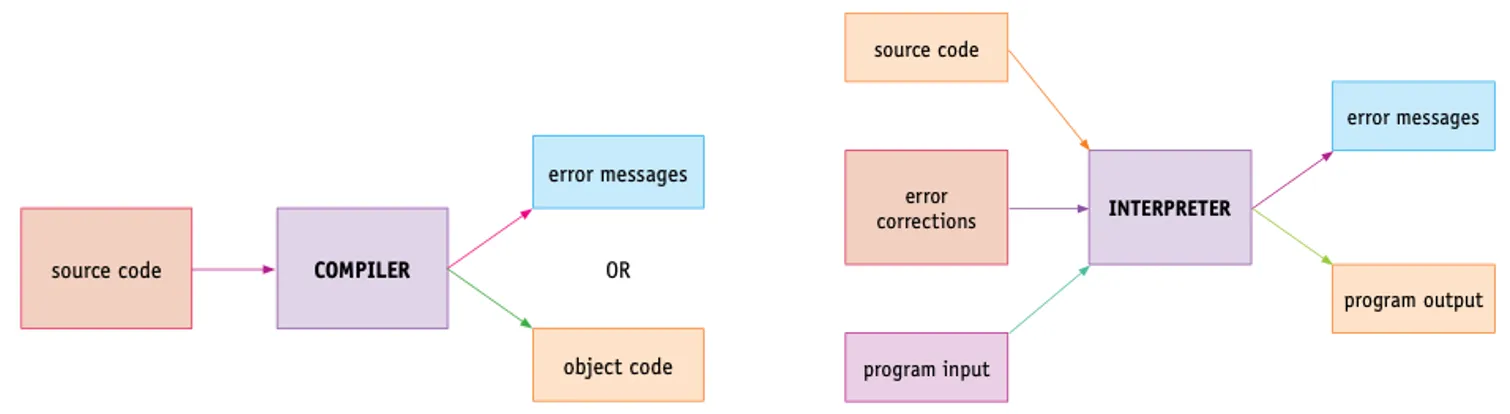
Virtual Machines

Introduction
It is important that virtual memory and virtual machines are not confused with each other – they are different concepts.
This section explains what virtual machines are and outlines some of the benefits and limitations.
Suppose you are using a PC running in a Windows 10 environment and you have downloaded some software that will only run on an Apple computer.
It is possible to emulate the running of the Apple software on the Windows PC (hardware) – this is known as a virtual machine.
The emulation will allow the Apple software to use all of the hardware on the host PC.
Effectively, a virtual machine runs the existing OS (called the host operating system) and oversees the virtual hardware using a guest operating system – in our example above, the host OS is Windows 10 and the guest OS is Apple.
The emulation engine is referred to as a hypervisor; this handles the virtual hardware (CPU, memory, HDD and other devices) and maps them to the physical hardware on the host computer.
Features
Guest operating system
This is the OS running in a virtual machine.
It controls the virtual hardware during the emulation.
This OS is being emulated within another OS (the host OS).
The guest OS is running under the control of the host OS software.
Host operating system
This is the OS that is controlling the actual physical hardware.
It is the normal OS for the host/physical computer.
The OS runs/monitors the virtual machine software.
Benefits and limitations of virtual machines
Benefits
The guest OS hosted on a virtual machine can be used without impacting anything outside the virtual machine; any other virtual machines and host computer are protected by the virtual machine software.
It is possible to run apps which are not compatible with the host computer/OS by using a guest OS which is compatible with the app.
Virtual machines are useful if you have old/legacy software which is not compatible with a new computer system/hardware.
Virtual machines are useful for testing a new OS or new app since they will not crash the host computer if something goes wrong
Limitations
You do not get the same performance running as a guest OS as you do when running the original system.
Building an in-house virtual machine can be quite expensive for a large company. They can also be complex to manage and maintain.