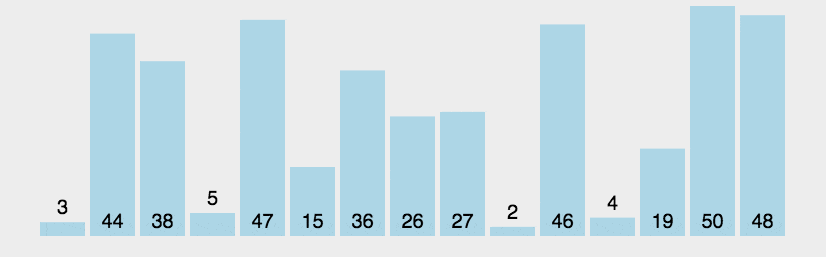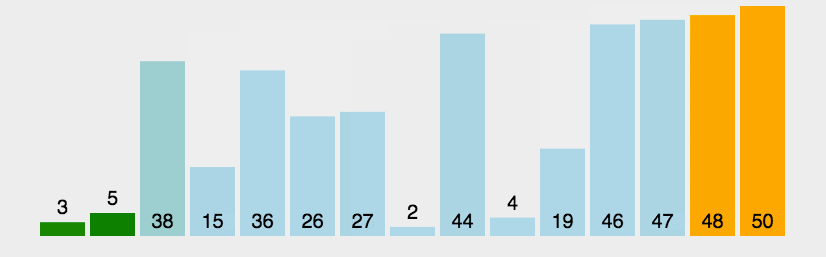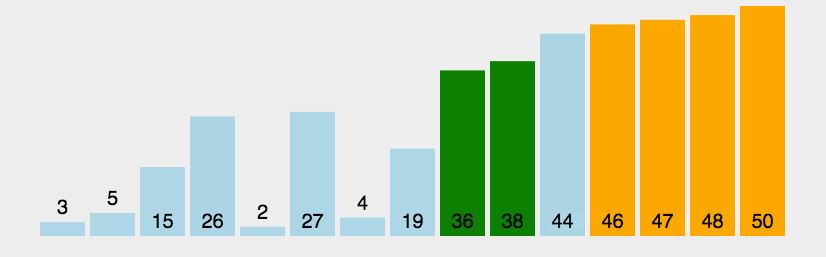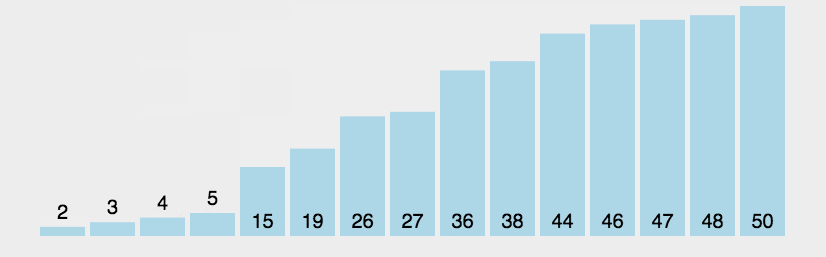Standard methods of solution
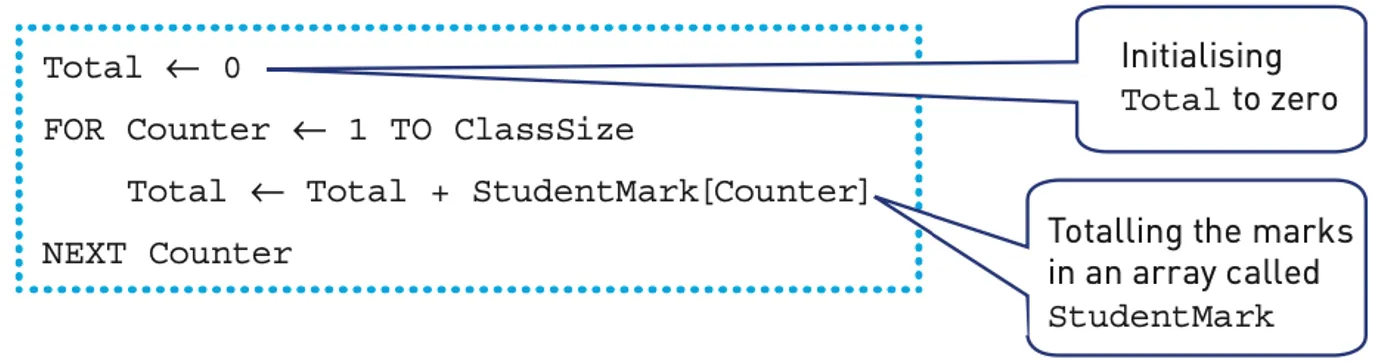
Totalling
Totalling means keeping a total that values are added to.
For example, keeping a running total of the marks awarded to each student in a class.
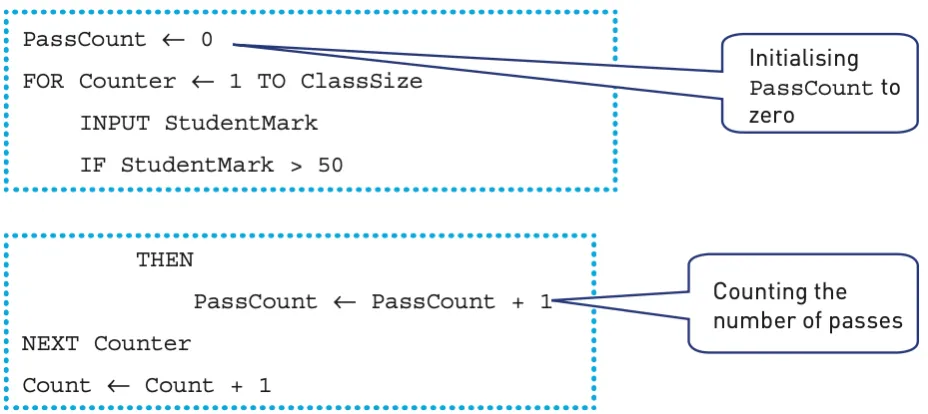
Counting
Keeping a count of the number of times an action is performed is another standard method.
For example, counting the number of students that were awarded a pass mark
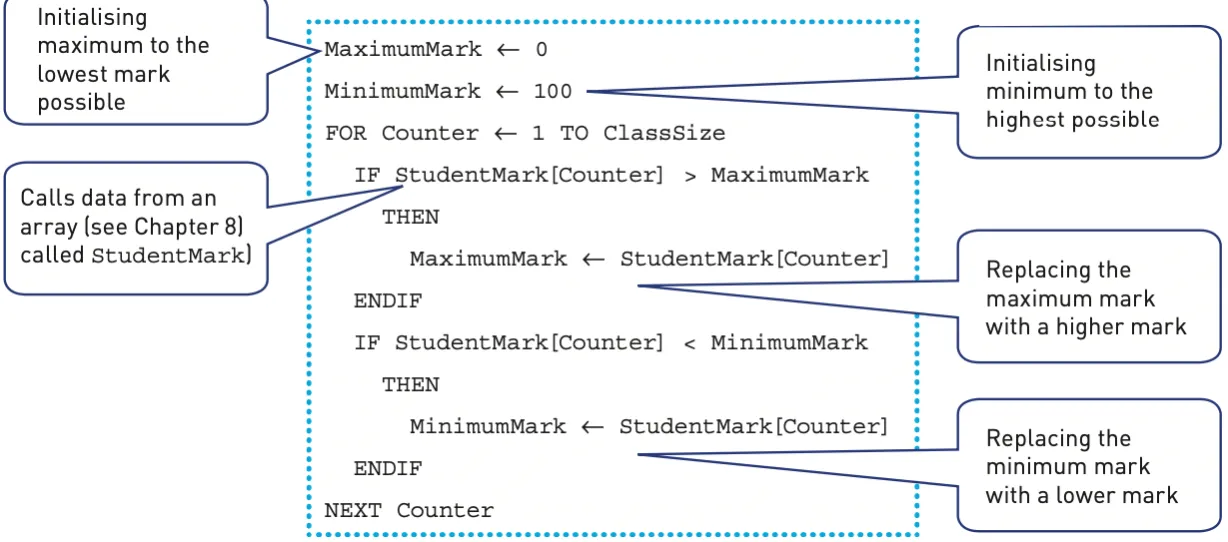
Maximum, minimum
Finding the largest and smallest values in a list are two standard methods that are frequently found in algorithms, for example, finding the highest and lowest mark awarded to a class of students.
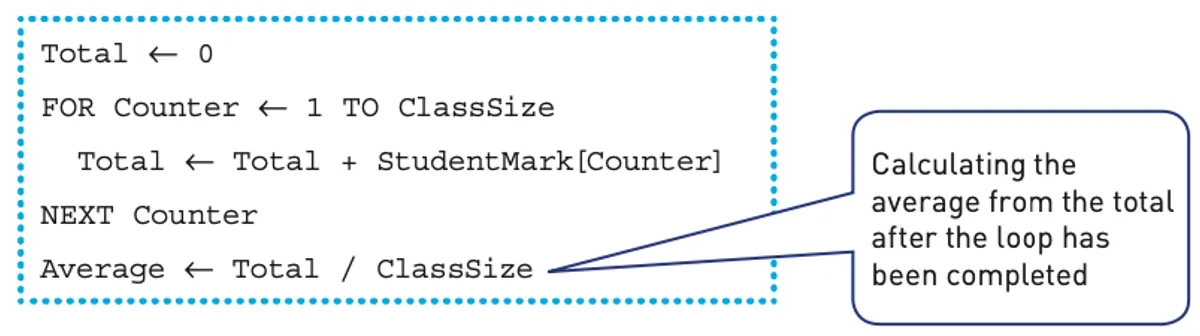
Average
Calculating the average (mean) of all the values in a list is an extension of the totalling method, for example, calculating the average mark for a class of students.
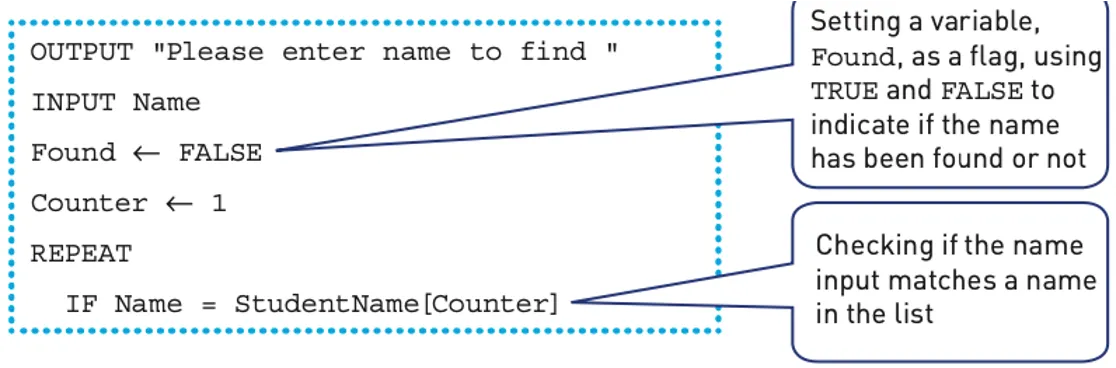
Linear search
Linear search inspects each item in a list in turn to see if the item matches the value searched for.
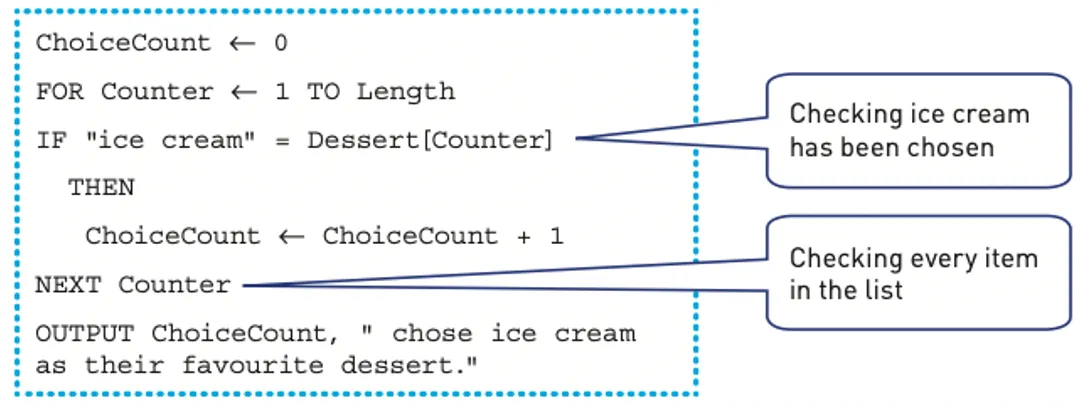
In this example, the search checks how many people chose ice cream as their favourite dessert, where several values in the list can be the same.
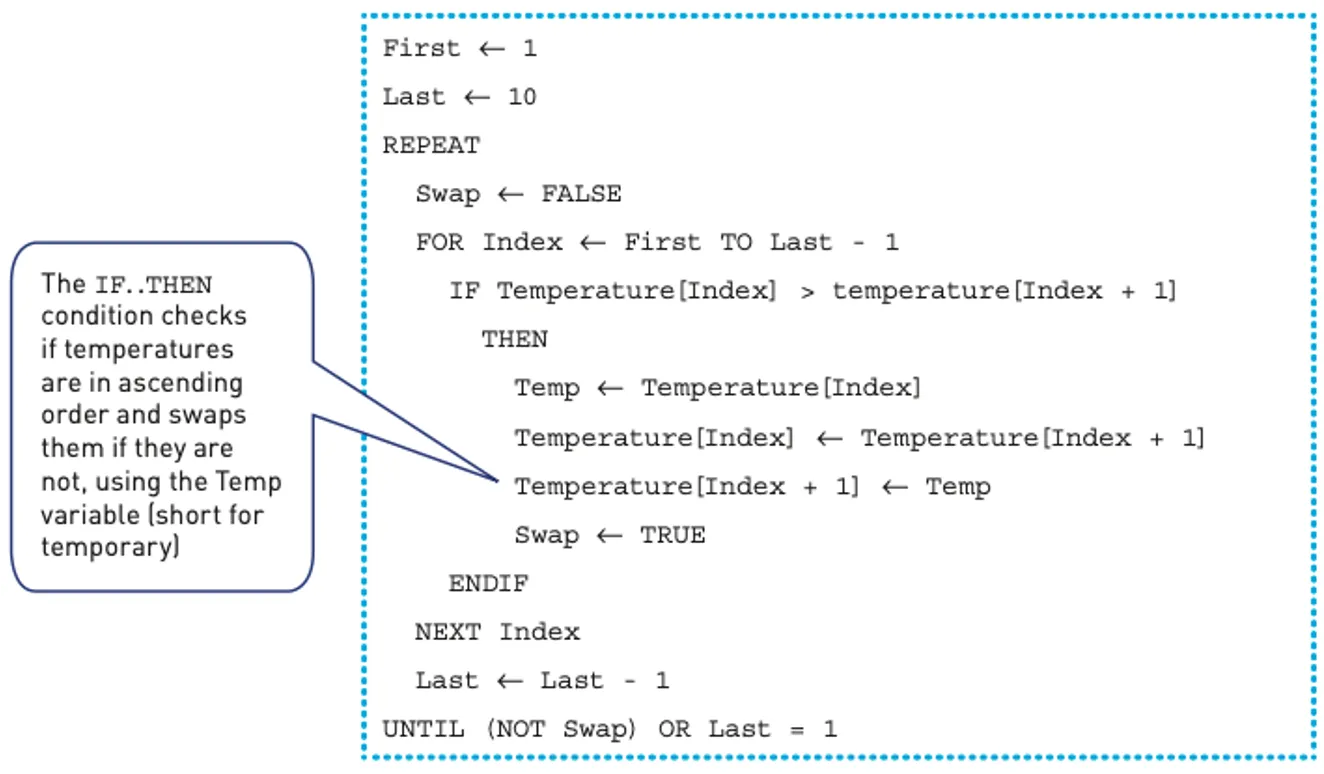
Bubble sort
This method of sorting is called a bubble sort.
Each element is compared with the next element and swapped if the elements are in the wrong order, starting from the first element and finishing with next-to-last element.
Once it reaches the end of the list, we can be sure that the last element is now in the correct place.
However, other items in the list may still be out of order.
Each element in the list is compared again apart from the last one because we know the final element is in the correct place.
This continues to repeat until there is only one element left to check or no swaps are made.