Number Systems
Understand binary
Any form of data needs to be converted to binary to be processed by a computer.
The basic building block in all computers is the binary number system.
Switch
Switch ON is 1 and OFF is 0.
Digit weight
Every one of us is used to the decimal or denary (base 10) number system. This uses the digits 0 to 9 which are placed in ‘weighted’ columns.
10000 | 1000 | 100 | 10 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
104 | 103 | 102 | 101 | 100 |
3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
Example: 3x10000 + 1x1000 + 4x100 + 2x10 + 1x1 = 31421
Binary to denary
Except for denary, we use binary(base 2) and hexadecimal(base 16) number system in the computer.
Denary value | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Binary value | 0000 | 0001 | 0010 | 0011 | 0100 | 0101 | 0110 | 0111 | 1000 | 1001 | 1010 | 1011 | 1100 | 1101 | 1110 | 1111 |
Hexadecimal value | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F |
The binary system uses 1s and 0s only which gives these corresponding weightings.
We can convert binary number to denary according to digit weightings.
128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Example: 1110 11102 = 128 + 64 + 32 + 8 + 4 + 2 = 23810
1010 0110
Hexadecimal to denary
The hexadecimal system is very closely related to the binary system.
Hexadecimal is a base 16 system.
Because it is a system based on 16 different digits, the numbers 0 to 9 and the letters A to F are used to represent hexadecimal digits.
A = 10, B = 11, C = 12, D = 13, E = 14 and F = 15.
We can convert hexadecimal number to denary according to digit weightings.
65536 | 4096 | 256 | 16 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
164 | 163 | 162 | 161 | 160 |
0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Example: 0112316 = 1x4096 + 1x256 + 2x16 + 3x1 = 438710
Convert the hexadecimal number 1A to decimal.
Convert the hexadecimal number FF to decimal.
Use of the hexadecimal system
Areas within computer science that hexadecimal is used should be identified:
Error codes
MAC addresses
IPv6 addresses
HTML colour codes
Hexadecimal is easier for humans to understand than binary, as it is a shorter representation of the binary.
When the memory contents are output to a printer or monitor, this is known as a memory dump.

Denary to binary
Converting from denary to binary is slightly more complex.
This method involves successive division by 2 until the result is 0; the remainders are then written from bottom to top to give the binary value.
Divider | Result | Remainder | Process |
|---|---|---|---|
2 | 107 | ||
2 | 53 | 1 | 107 ➗ 2 = 53 ……1 |
2 | 26 | 1 | 53 ➗ 2 = 26 ……1 |
2 | 13 | 0 | 26 ➗ 2 = 13 ……0 |
2 | 6 | 1 | 13 ➗ 2 = 6 ……1 |
2 | 3 | 0 | 6 ➗ 2 = 3 ……0 |
2 | 1 | 1 | 3 ➗ 2 = 1 ……1 |
0 | 1 | 1 ➗ 2 = 0 ……1 |
Example: 10710 = 110 10112
Convert the decimal number 10 to binary.
Convert the decimal number 23 to binary.
Denary to hexadecimal
Converting from denary to hexadecimal is slightly similar with denary to binary.
This method involves successive division by 16; the remainders are then written from bottom to top to give the hexadecimal value.
Divider | Result | Remainder | Process |
|---|---|---|---|
16 | 2004 | ||
16 | 125 | 4 | 2004 ➗ 16 = 125 ……4 |
16 | 7 | 13(D) | 125 ➗ 16 = 7 ……13(D) |
16 | 0 | 7 | 7 ➗ 16 = 0 ……7 |
Example: 200410 = 7D416
Binary to hexadecimal
Since 16 = 24, four binary digits are equivalent to each hexadecimal digit.
Binary value | 0000 | 0001 | 0010 | 0011 | 0100 | 0101 | 0110 | 0111 | 1000 | 1001 | 1010 | 1011 | 1100 | 1101 | 1110 | 1111 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Hexadecimal value | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F |
Denary value | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
Example: $1111100001_2 = 0011\ 1110\ 0001_2 = 3E1_{16}$
Convert the decimal number 255 to hexadecimal.
Convert the decimal number 16 to hexadecimal.
Hexadecimal to binary
Since 16 = 24, one hexadecimal digit are equivalent to four binary digits.
Example: 45A16 = 0100 0101 10102
Convert the hexadecimal number A to binary.
Convert the hexadecimal number F to binary.
Binary addition
bianry addtion
0 + 0 = 0
1 + 0 = 1 (sum 1 and carry 0)
1 + 1 = 10 (sum 0 and carry 1 )
1 + 1 + (carry 1) = 11= sum 1 and carry 1
Add 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 (37 in denary) and 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 (58 in denary).
-128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
37 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
+ | ||||||||
58 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
= | ||||||||
Carry | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Sum | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
The sum is 0101 1111, which is 95 in denary.
Overflow error
Add 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 (82 in denary) and 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 (69 in denary).
-128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
82 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
+ | ||||||||
69 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
= | ||||||||
Carry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Sum | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
The sum is 1001 0111, which is -105 (Incorrect)
Overflow error
The expected answer for 82 + 69 is 151, which is out of range for the 8 bits register (-128~127), this is known as an overflow error.
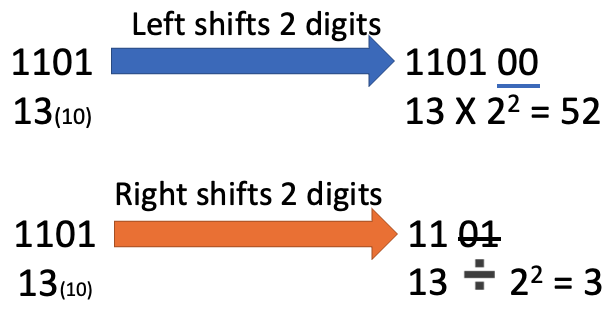
Logical shifts
The positive binary integer is multiplied or divided according to the shift performed.
Bits shifted from the end of the register are lost and zeros are shifted in at the opposite end of the register.
The most significant bit(s) or least significant bit(s) are lost.