Data Storage And Compression
Measurement of the size of computer memories
TIP
A binary digit is referred to as a BIT. 4 bits are 1 NIBBLE. 8 bits are 1 BYTE.
Storage Device
Measurement | Number of bytes |
|---|---|
1 kilobyte(1 KB) | 103 |
1 megabyte(1 MB) | 106 |
1 gigabyte(1 GB) | 109 |
1 terabyte(1 TB) | 1012 |
1 petabyte(1 PB) | 1015 |
Computer System
Measurement | Number of bytes |
|---|---|
1 kibibyte(1 KiB) | 210 |
1 mebibyte(1 MiB) | 220 |
1 gibibyte(1 GiB) | 230 |
1 tebibyte(1 TiB) | 240 |
1 pebibyte(1 PiB) | 250 |
KB vs KiB
KB is used in factory and Kib is used in computer system.
Compression types
Lossless compression reduces the file size without permanent loss of data, e.g. run length encoding (RLE)
Lossy compression reduces the file size by permanently removing data, e.g. reducing resolution or colour depth, reducing sample rate or resolution.
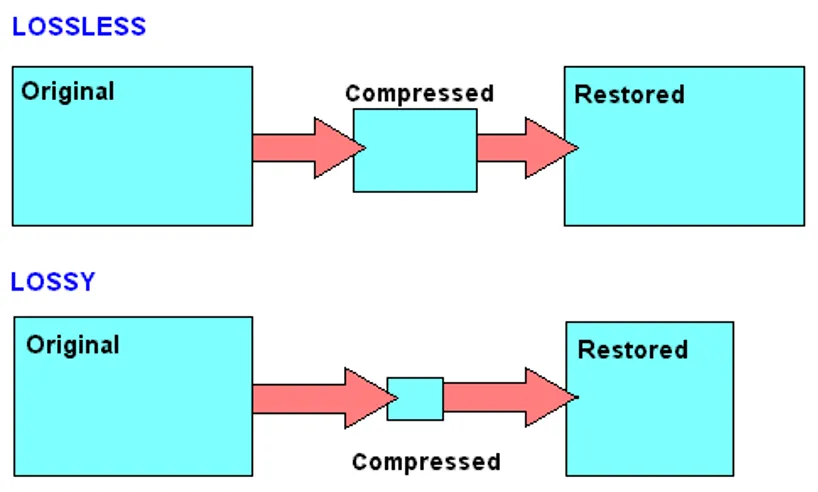
How RLE works
The original string contains 32 characters and would occupy 32 bytes of storage.
The coded version contains 18 values and would require 18 bytes of storage.

Also works for images
Audio Compression
MPEG-3 (MP3) uses technology known as audio compression to convert music and other sounds into an MP3 file format which use lossy compression.
Perceptual music shaping removes certain sounds:
frequencies that are outside the human hearing range
if two sounds are played at the same time, only the louder one can be heard by the ear, so the softer sound is eliminated.
Image Compression
When a photographic file is compressed, both the file size and quality of image are reduced.
A common file format for images is JPEG, which uses lossy file compression.
Compression benefits
less bandwidth required
less storage space required
shorter transmission time